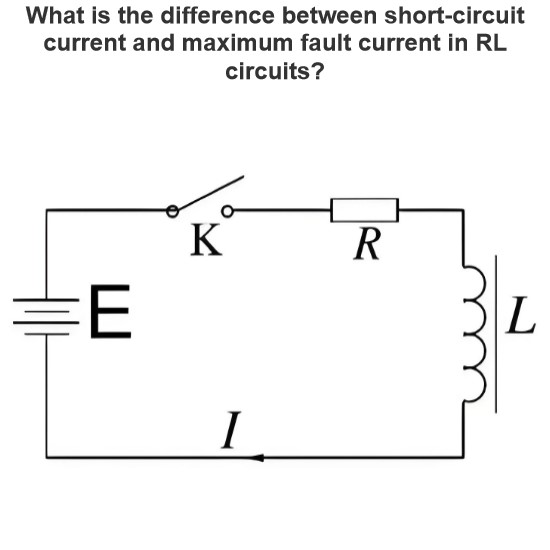
What are the purposes of using ABCD parameters in the analysis of transmission lines?
Purpose of Using Z, Y, and ABCD Parameters in Transmission Line Analysis.
In transmission line analysis, the use of Z (impedance), Y (admittance), and ABCD parameters serves to conveniently describe and analyze the behavior of transmission lines. Each set of parameters has its specific applications and advantages. Below is a detailed explanation of the purpose of each parameter:
1. Impedance Parameters (Z)
Purpose
Describe Input Characteristics: Impedance parameters are used to describe the input impedance of a transmission line at a given frequency. This is crucial for matching the impedance of the load and source to maximize power transfer.
Analyze Reflection and Transmission: Impedance parameters can be used to calculate reflection coefficients and transmission coefficients, thereby analyzing the reflection and transmission behavior of signals on the transmission line.
Applications
Impedance Matching: Ensure that the input impedance of the transmission line matches the load impedance to minimize reflections and improve transmission efficiency.
Reflection Coefficient Calculation: Use impedance parameters to calculate the reflection coefficient and evaluate the reflection of signals on the transmission line.
2. Admittance Parameters (Y)
Purpose
Describe Output Characteristics: Admittance parameters are used to describe the output admittance of a transmission line at a given frequency. This is useful for analyzing the current and voltage distribution at the end of the transmission line.
Analyze Parallel Connections: Admittance parameters are particularly suitable for analyzing multiple transmission lines connected in parallel.
Applications
Parallel Network Analysis: In cases where multiple transmission lines are connected in parallel, using admittance parameters simplifies the analysis of the network.
Output Characteristic Evaluation: Evaluate the current and voltage distribution at the end of the transmission line to ensure proper load matching.
3. ABCD Parameters
Purpose
Describe Overall Characteristics:
ABCD parameters (also known as transmission matrix or chain parameters) are used to describe the overall characteristics of a transmission line, including the relationship between voltage and current. They are convenient for representing cascaded connections of transmission lines.
Analyze Cascaded Networks:
ABCD parameters are particularly useful for analyzing multiple segments of transmission lines connected in series, allowing for easy calculation of the overall system's transmission characteristics.
Applications
Cascaded Transmission Line Analysis: In cases where multiple segments of transmission lines are cascaded, using
ABCD parameters simplifies the overall analysis of the system.
Transmission Characteristic Calculation: Calculate transmission characteristics such as voltage gain, current gain, input impedance, and output impedance of the transmission line.
Network Synthesis: In designing transmission line networks,
ABCD parameters can help synthesize the desired transmission characteristics.
Summary
Impedance Parameters (Z): Mainly used to describe the input characteristics of transmission lines, analyze reflection and transmission behavior, and perform impedance matching.
Admittance Parameters (Y): Mainly used to describe the output characteristics of transmission lines, analyze parallel connections, and evaluate current and voltage distribution at the end of the line.
ABCD Parameters: Mainly used to describe the overall characteristics of transmission lines, analyze cascaded networks, and calculate transmission characteristics.
Each set of parameters has its specific applications and advantages, and choosing the appropriate parameters can simplify the analysis and design process of transmission lines.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.