What is a Wheatstone Bridge Circuit?
What is a Wheatstone Bridge Circuit?
Wheatstone Bridge Definition
A Wheatstone Bridge is widely used to measure electrical resistance accurately. It includes two known resistors, one variable resistor, and one unknown resistor connected in a bridge form. By adjusting the variable resistor until the galvanometer reads zero current, the ratio of the known resistors matches the ratio of the variable resistor and the unknown resistor. This allows easy measurement of the unknown electrical resistance.
Wheatstone Bridge Theory
The Wheatstone bridge circuit has four arms: AB, BC, CD, and AD, each with resistors labeled P, Q, S, and R, respectively. This arrangement forms the bridge needed for accurate resistance measurement.
The resistors P and Q are known fixed resistances and are called the ratio arms. A sensitive galvanometer is connected between points B and D through switch S2.
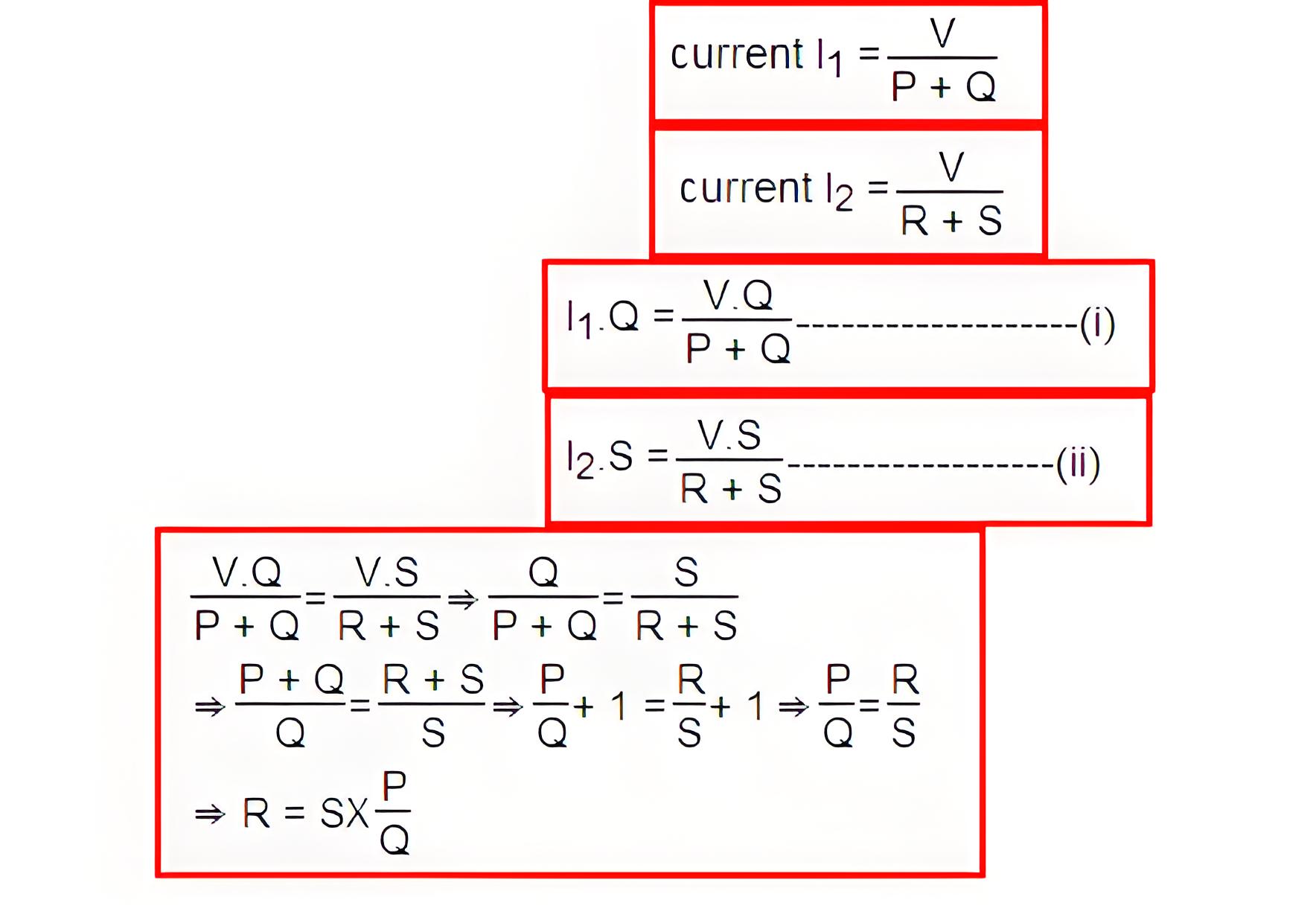
The Wheatstone bridge’s voltage source connects to points A and C via switch S1. A variable resistor S is between points C and D. Adjusting S changes the potential at point D. Currents I1 and I2 flow through paths ABC and ADC, respectively.
If we vary the electrical resistance value of arm CD the value of current I2 will also be varied as the voltage across A and C is fixed. If we continue to adjust the variable resistance one situation may comes when voltage drop across the resistor S that is I2. S is becomes exactly equal to voltage drop across resistor Q that is I1.Q. Thus the potential at point B becomes equal to the potential at point D hence potential difference between these two points is zero hence current through galvanometer is nil. Then the deflection in the galvanometer is nil when the switch S2 is closed.
Now, from Wheatstone bridge circuit and Now potential of point B in respect of point C is nothing but the voltage drop across the resistor Q and this isAgain potential of point D in respect of point C is nothing but the voltage drop across the resistor S and this isEquating, equations (i) and (ii) we get,
Here in the above equation, the value of S and P⁄Q are known, so value of R can easily be determined.
The electrical resistances P and Q of the Wheatstone bridge are made of definite ratio such as 1:1; 10:1 or 100:1 known as ratio arms and S the rheostat arm is made continuously variable from 1 to 1,000 Ω or from 1 to 10,000 Ω.
The above explanation is most basic Wheatstone bridge theory.
Welcome to our electricity community! Established to facilitate the exchange and cooperation in the electricity industry and bridge professionals, enthusiasts, and related enterprises.