What is Inductance?
What is Inductance?
Inductance definition
A property of a conductor measured by the ratio of the induced electromotive force or voltage in the conductor to the rate of change of the current that produces it. A constant current produces a stable magnetic field, a changing current (AC) or a fluctuating DC produces a changing magnetic field, which in turn induces electromotive force on a conductor in this magnetic field. The magnitude of the induced electromotive force is proportional to the rate of change of current. The scale factor is called inductance and is represented by the symbol L in Henry (H).
Inductance classification
Self-inductance When a current passes through the coil, a magnetic field is generated around the coil. When the current in the coil changes, the magnetic field around it also produces a corresponding change, and this change in the magnetic field can cause the coil itself to generate induced electromotive force.
Mutual inductance
When two inductors are close to each other, the magnetic field change of one inductor will affect the other inductor.
Self-inductance calculation formula in linear magnetic medium
Self-induction of a long solenoid:
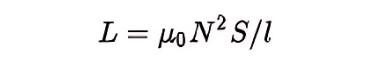
Where l is the length of the solenoid; S is the cross-sectional area of the solenoid; N is the total number of turns.
Self-inductance of a coreless ring winding coil
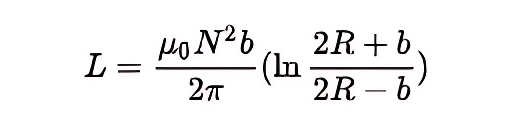
Where b is the side length of the square section; N is the total number of turns.
Self-inductance of coaxial cable
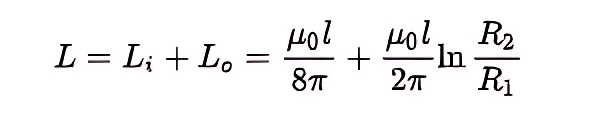
Where R1 and R2 are the radii of the inner and outer conductors of the coaxial cable respectively; l is the cable length; Li and Lo are called the internal and external self-inductance of a coaxial cable, respectively, where the value of the internal self-inductance Li is only related to the length of the inner conductor of the cable, not its radius.
Self-induction of a two-wire transmission line
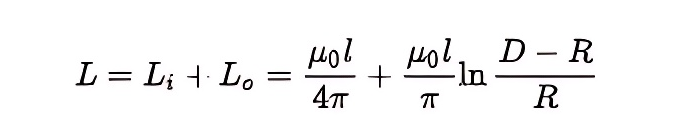
Where R is the radius of the two wires; l is the transmission line length; D is the distance between the axes of two wires.
Calculation formula of mutual inductance in linear magnetic media
Mutual inductance between two coaxial length solenoids
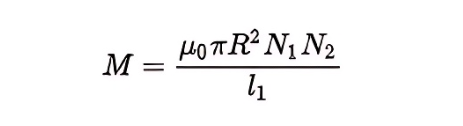
In the formula, N1 and N2 are the turns of the two solenoids respectively.
Mutual inductance between two pairs of transmission lines
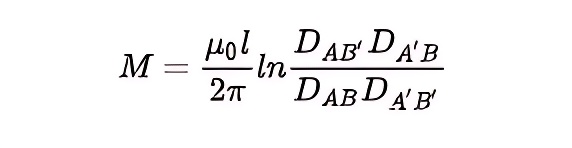
In the formula, DAB ', DA 'B, DAB and DA' B 'are respectively the distance between the corresponding wires between the two pairs of transmission lines, and l is the length of the transmission line.
We aim to gather electrical knowledge and share it with others.

