What is Silicon Semiconductor?
What is Silicon Semiconductor?
Silicon Semiconductor Definition
A silicon semiconductor is defined as a material that has an electrical conductivity value between that of a conductor and an insulator, and whose conductivity can be altered by introducing impurities or applying external fields or light. Silicon is the most widely used semiconductor material in modern electronics, especially in power devices, integrated circuits, photovoltaic cells, and transistors.
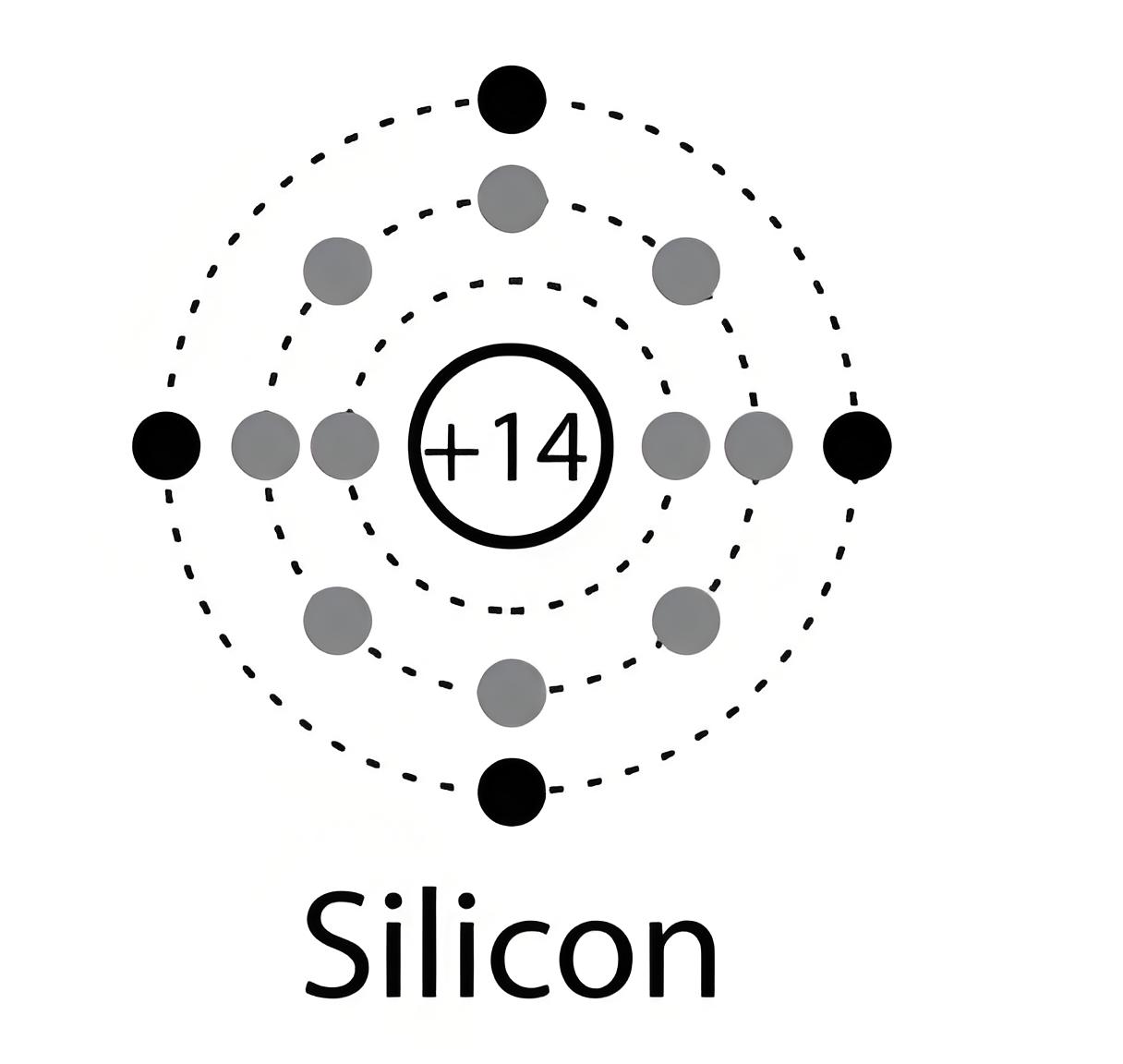
Thermal and Electrical Properties
Silicon has a high melting point and a low band gap energy, making it suitable for high-temperature and power applications.
Doping for Conductivity
Doping silicon with impurities creates n-type or p-type semiconductors, crucial for electronic devices.
Applications in Electronics
Power devices: Silicon is used to make diodes, thyristors, IGBTs, MOSFETs, and other devices that can handle high voltages and currents in power conversion, transmission, distribution, and control systems.
Integrated circuits: Silicon is used to fabricate microchips that integrate millions or billions of transistors and other components on a single chip. These chips are used for various purposes, such as memory, logic, processing, communication, and sensing.
Photovoltaic cells: Silicon is used to convert sunlight into electricity in solar cells. Silicon-based solar cells are the most common and efficient type of photovoltaic devices.
Transistors: Silicon is used to make bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs), which are the basic building blocks of modern electronics. These transistors can amplify or switch electrical signals in various circuits and systems.
Advantages of Silicon
It is compatible with various fabrication techniques, such as lithography, etching, doping, oxidation, deposition, and bonding.
It has a high-quality crystalline structure and purity, which reduces defects and improves performance.
It has a large market share and economy of scale, which lowers the cost and increases the availability of silicon-based devices.
It has a wide range of applications and functions, which makes it versatile and adaptable to different needs and demands.
Conclusion
A silicon semiconductor has intermediate electrical conductivity, modifiable by doping or external stimuli. It is the most widely used semiconductor in modern electronics due to its availability, durability, conductivity, compatibility, quality, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. Silicon semiconductors are used in power devices, integrated circuits, photovoltaic cells, transistors, and more, with applications in communication, computing, control, sensing, and energy conversion.
Welcome to our electricity community! Established to facilitate the exchange and cooperation in the electricity industry and bridge professionals, enthusiasts, and related enterprises.