How do you calculate synchronous speed from frequency in an induction machine?
The synchronous speed (Synchronous Speed) of an induction motor is the speed at which the motor would operate under ideal conditions (i.e., with no slip). The synchronous speed depends on the frequency of the power supply and the number of pole pairs in the motor. Here is how to calculate the synchronous speed:
Calculation Formula
The synchronous speed ns can be calculated using the following formula:
ns= (120×f)/p
where:
ns is the synchronous speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).
f is the frequency of the power supply, measured in hertz (Hz).
p is the number of pole pairs in the motor.
Explanation
Power Supply Frequency f:
The power supply frequency is the frequency of the alternating current supplied to the motor, typically 50 Hz or 60 Hz.
Number of Pole Pairs p:
The number of pole pairs is the number of pairs of magnetic poles in the stator winding of the motor. For example, a 4-pole motor has 2 pole pairs, so p=2.
Synchronous Speed ns:
The synchronous speed is the speed at which the motor would run under ideal conditions (i.e., with zero slip). In actual operation, the motor's actual speed will be slightly less than the synchronous speed due to slip.
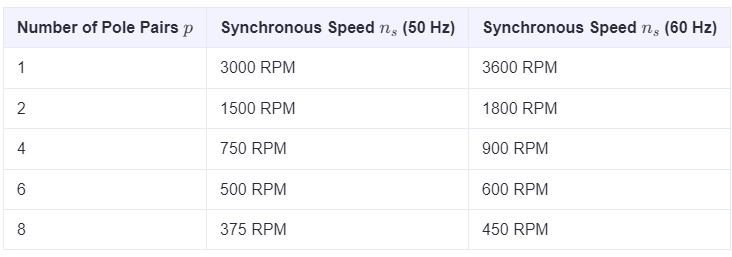
Synchronous Speed for Different Pole Pairs
The following table shows the synchronous speeds for common numbers of pole pairs, assuming power supply frequencies of 50 Hz and 60 Hz:
Summary
By using the formula ns= (120×f)/p, you can easily calculate the synchronous speed of an induction motor based on the power supply frequency and the number of pole pairs. The synchronous speed is an important parameter in motor design and performance analysis, helping to understand the motor's operating characteristics.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.