Construction of Synchronous Motor
Synchronous Motor Definition
A synchronous motor is defined as a motor that runs at synchronous speed, determined by supply frequency and the number of poles.

Where, Ns = synchronous speed, f = supply frequency and p = number of poles.
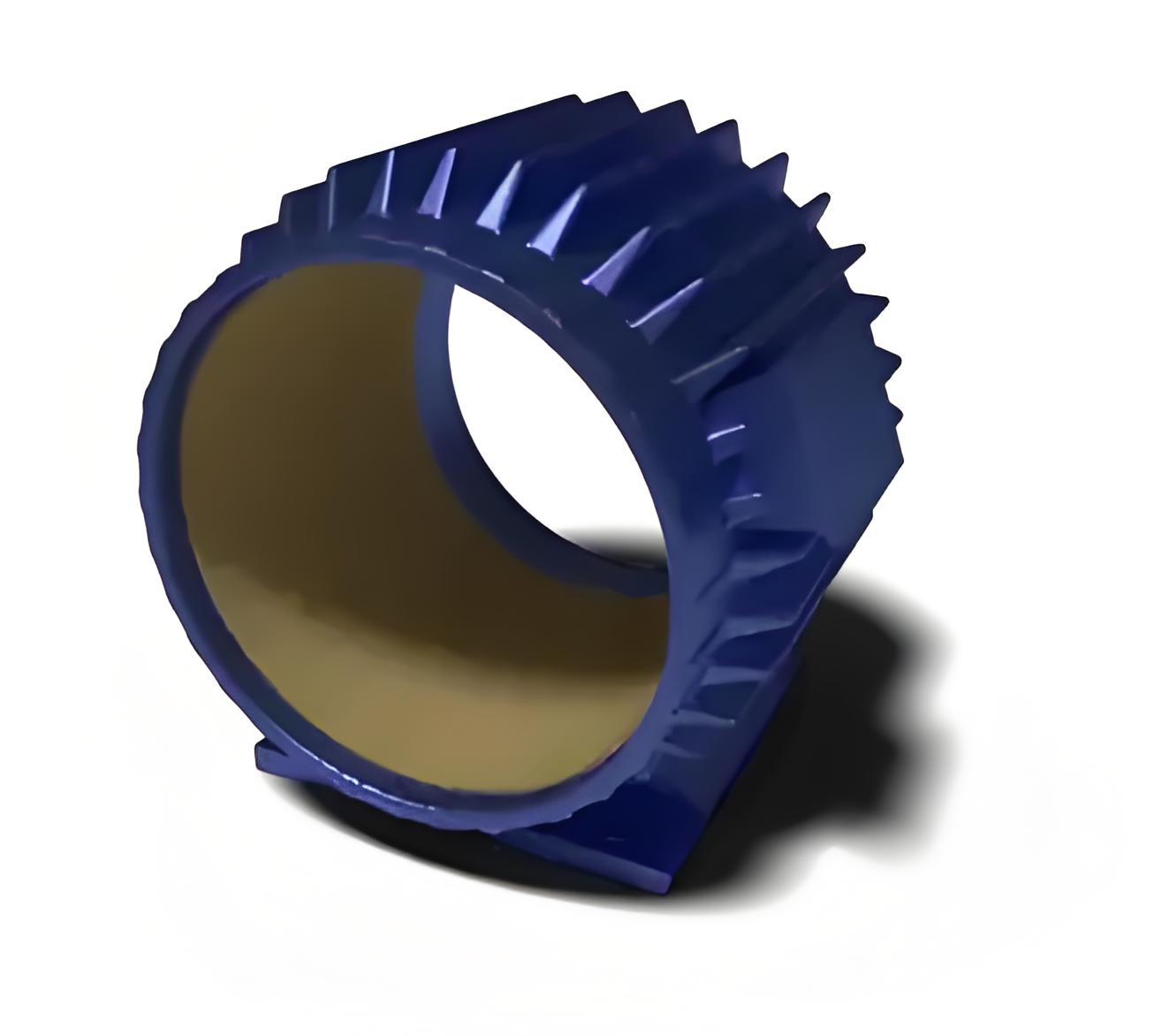
Stator Components
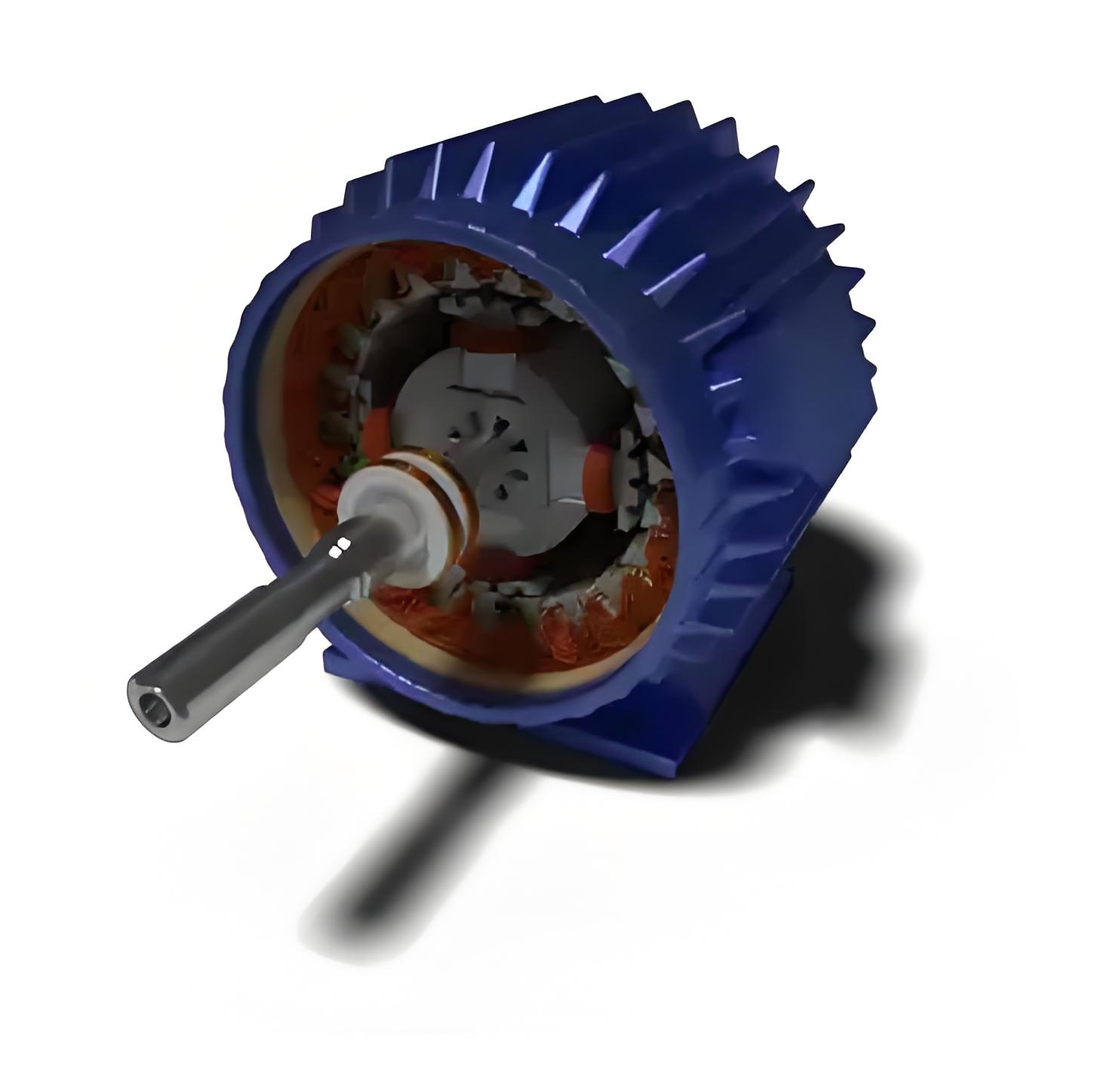
Stator Frame
The stator frame is the outer part of the motor, made from cast iron. It protects all the internal components of the motor.
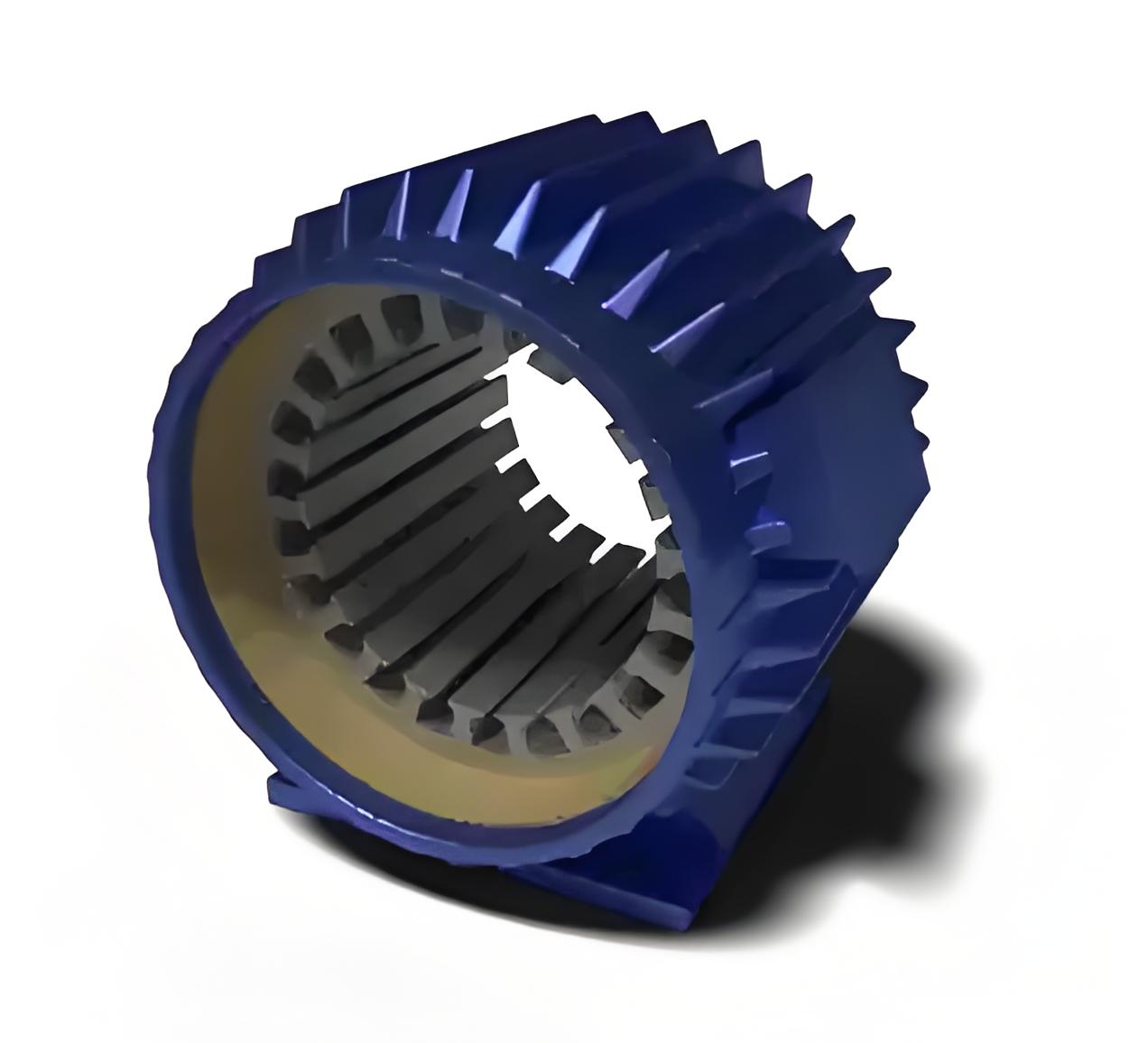

Stator Core
The stator core is made from thin silicon laminations with an insulating surface coating. This reduces hysteresis and eddy current losses. Its main role is to provide an easy path for magnetic lines and to hold the stator windings.
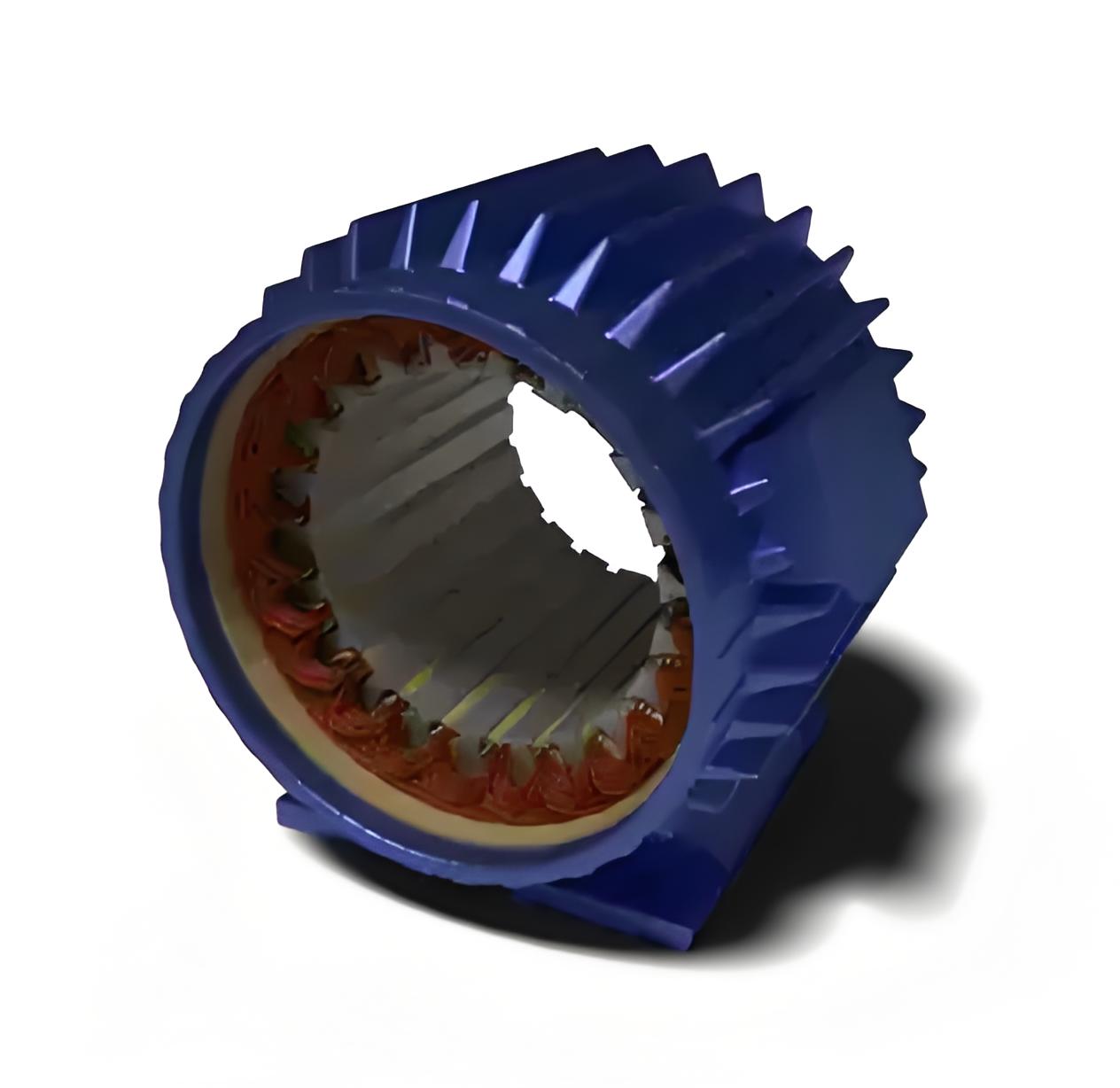
Stator Winding
The stator core has cuts on the inner periphery to accommodate the stator windings. The stator windings could be either three-phase windings or single phase windings.
Enamelled copper is used as the winding material. In the case of 3 phase windings, the windings are distributed over several slots. This is done to produce a sinusoidal distribution of EMF.
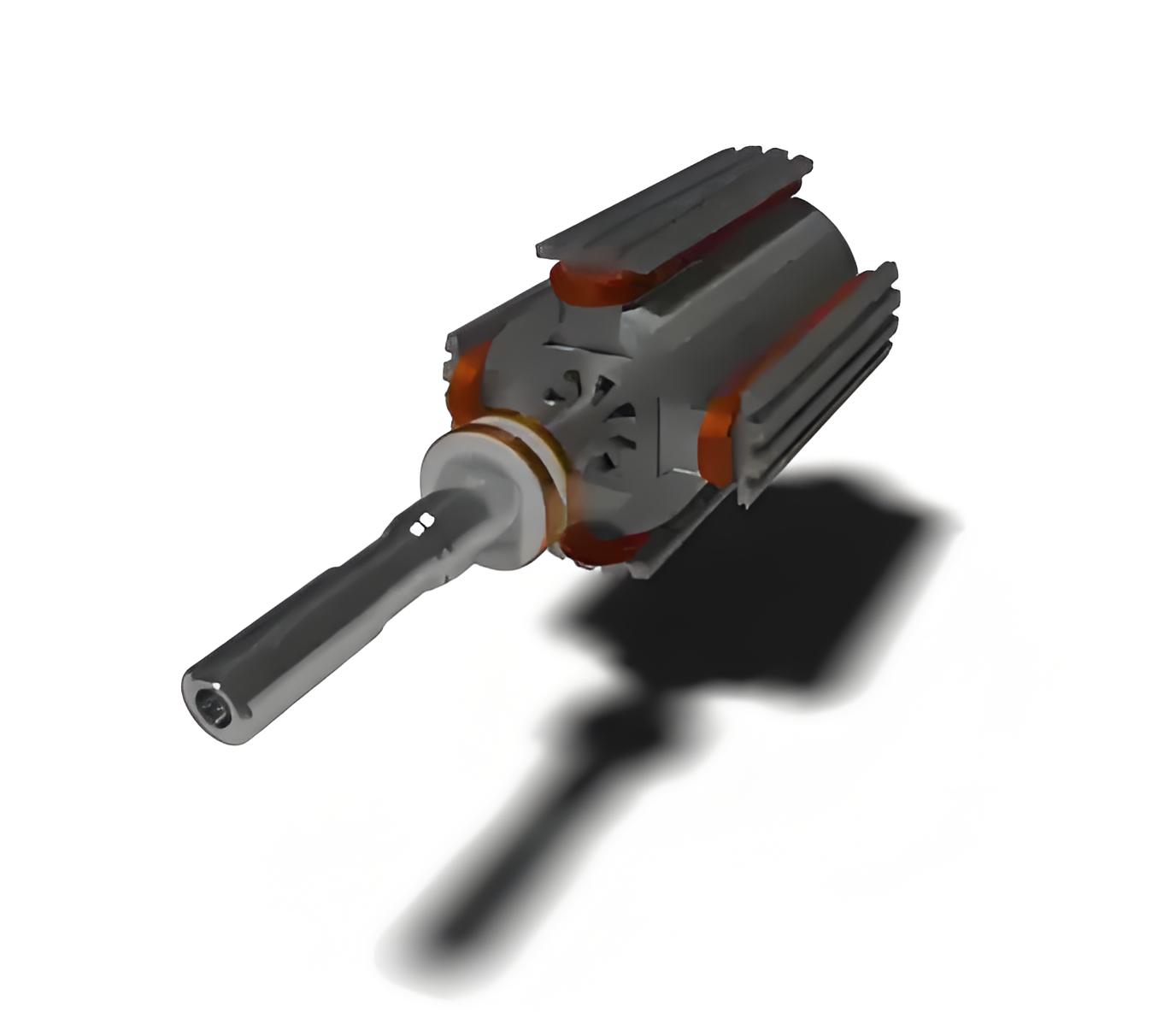

Rotor Types
Salient Pole Type
The salient pole type rotor consists of poles projecting out from the rotor surface. It is made up of steel laminations to reduce eddy current losses. A salient pole machine has a non-uniform air gap. The gap is maximum between the poles and is minimum at the pole centres. They are generally used for medium and low-speed operations as they have a large number of poles. They contain damper windings which are used for starting the motor.
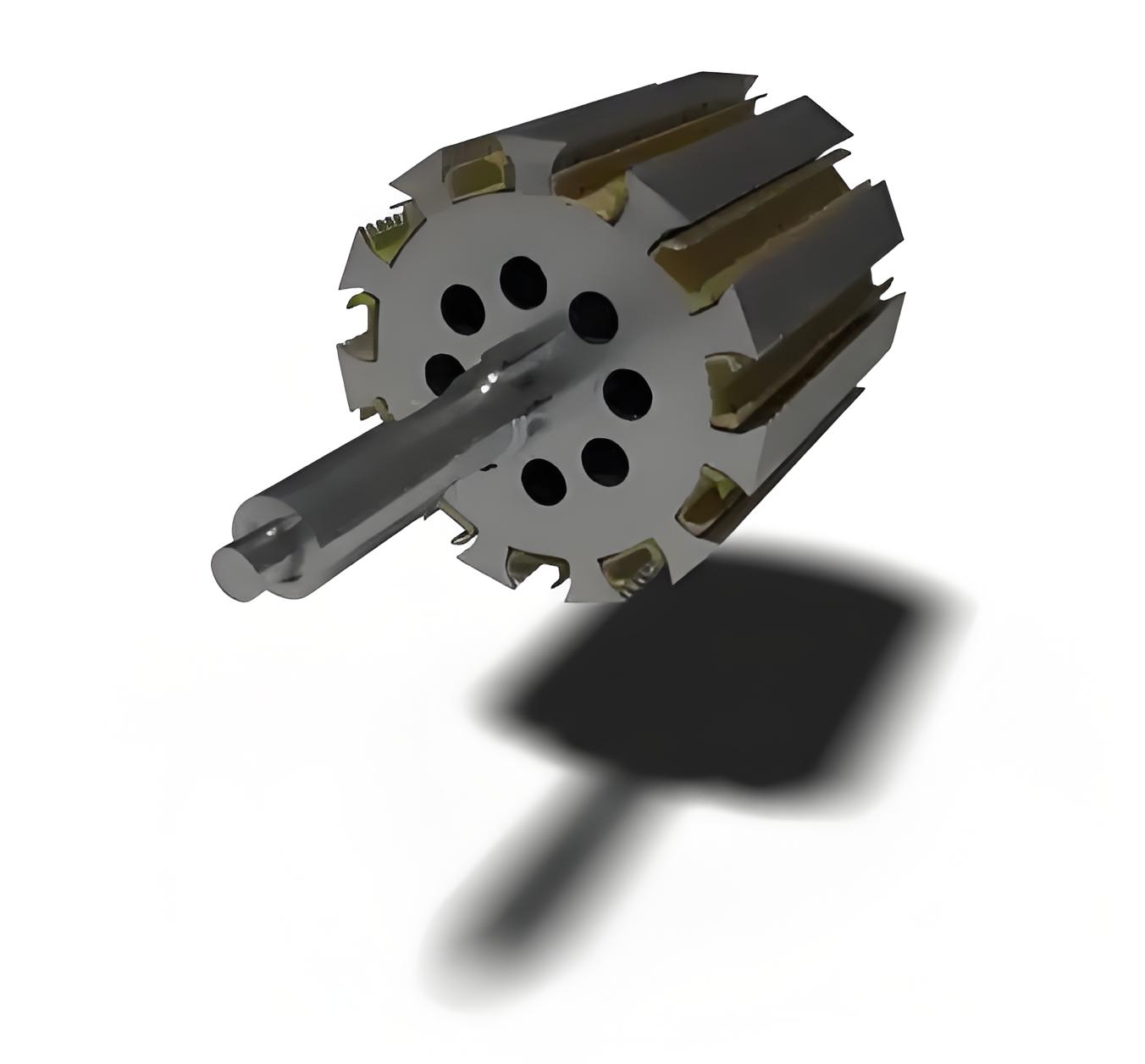
Cylindrical Rotor Type
A cylindrical rotor is made from solid high-grade steel, specifically nickel chrome molybdenum. The poles are formed by the current in the windings. These rotors are used in high-speed applications because they have fewer poles and produce less noise and windage losses due to their uniform air gap. DC supply is provided to the rotor windings through slip-rings, making them act like poles when excited.

Welcome to our electricity community! Established to facilitate the exchange and cooperation in the electricity industry and bridge professionals, enthusiasts, and related enterprises.