What is Deep Bar Double Cage Induction Motor?
What is Deep Bar Double Cage Induction Motor?
Deep bar double cage induction motor definition
Deep-bar double-cage induction motors are defined as motors that use double-layer rotors to enhance starting torque and efficiency.
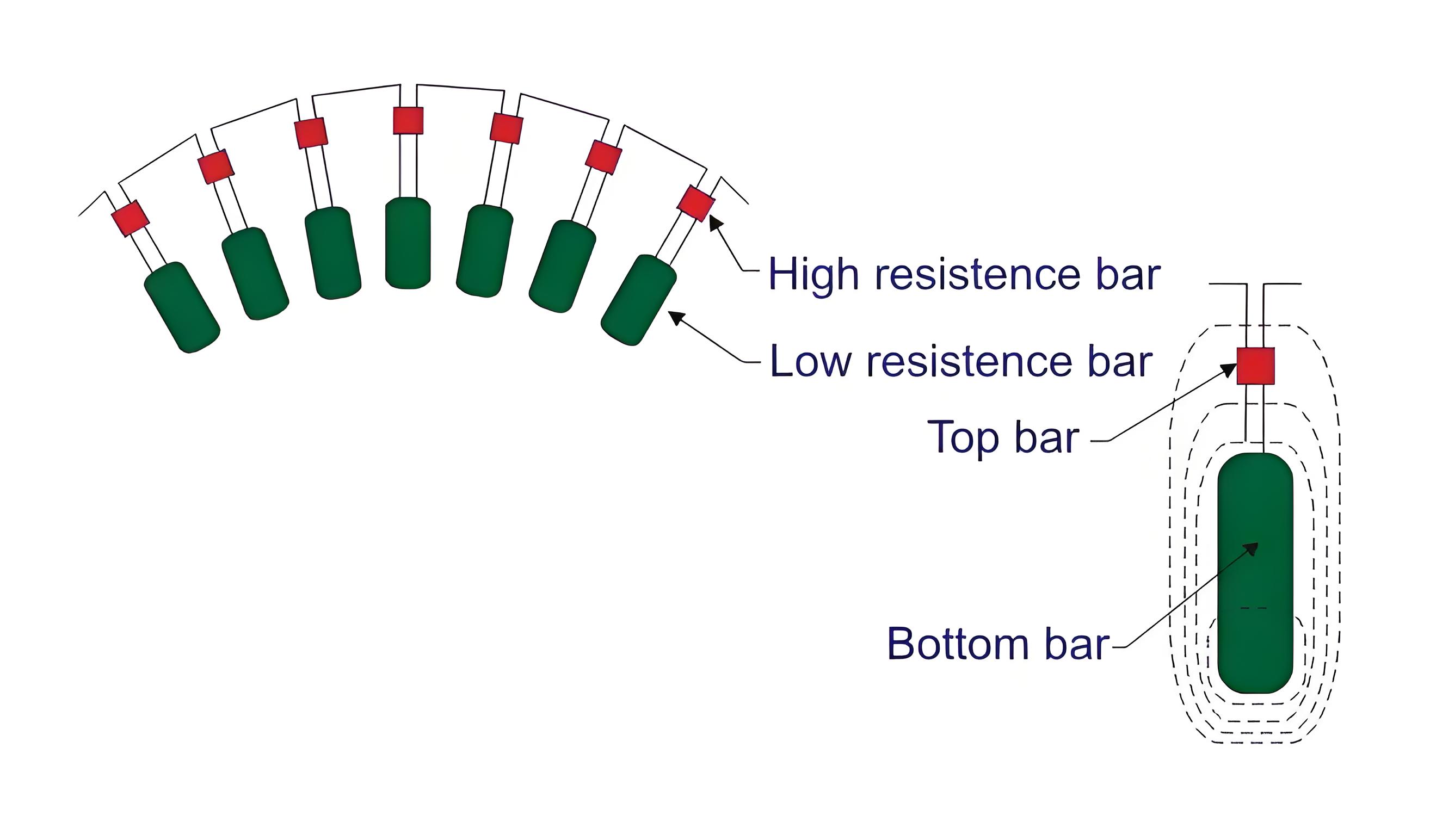
The structure of the double cage rotor
In the deep rod, the double cage rotor rod is divided into two layers.
The outer layer contains bars with small cross sections and high resistance, short-circuited at both ends. This results in low flux linkage and low inductance. The high resistance of the outer cage increases the starting torque by providing a high resistance reactance ratio. The inner layer has a bar with large cross section and low resistance. These bars are embedded in the iron, resulting in high flux linkage and high inductance. Low resistance to inductive reactance ratio makes the inner layer effective under operating conditions.
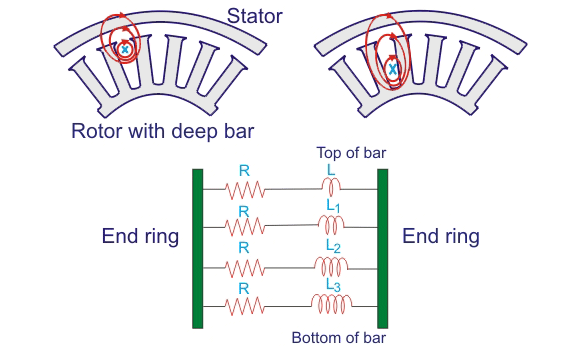
Working principle
At rest, the inside and outside rods sense voltage and current at the same power frequency. It is now the case that the inductive reactance (XL= 2πfL) is provided more in the deep or inside rods due to the skin effect of the alternating quantities (i.e. voltage and current). Therefore, current attempts to flow through the outer rotor rod.
The outer rotor provides greater resistance, but less inductive resistance. The ultimate resistance is slightly higher than that of a single rod rotor. The higher the resistance value of the rotor, the greater the torque generated at starting. When the rotor speed of deep-bar double-cage induction motor increases, the frequency of induced electromotive force and current in the rotor decreases gradually. Therefore, the inductive reactance is reduced in the inner bar or deep bar, and the current as a whole faces smaller inductive reactance and smaller resistance. No more torque is needed now because the rotor has reached full speed of its operating torque.
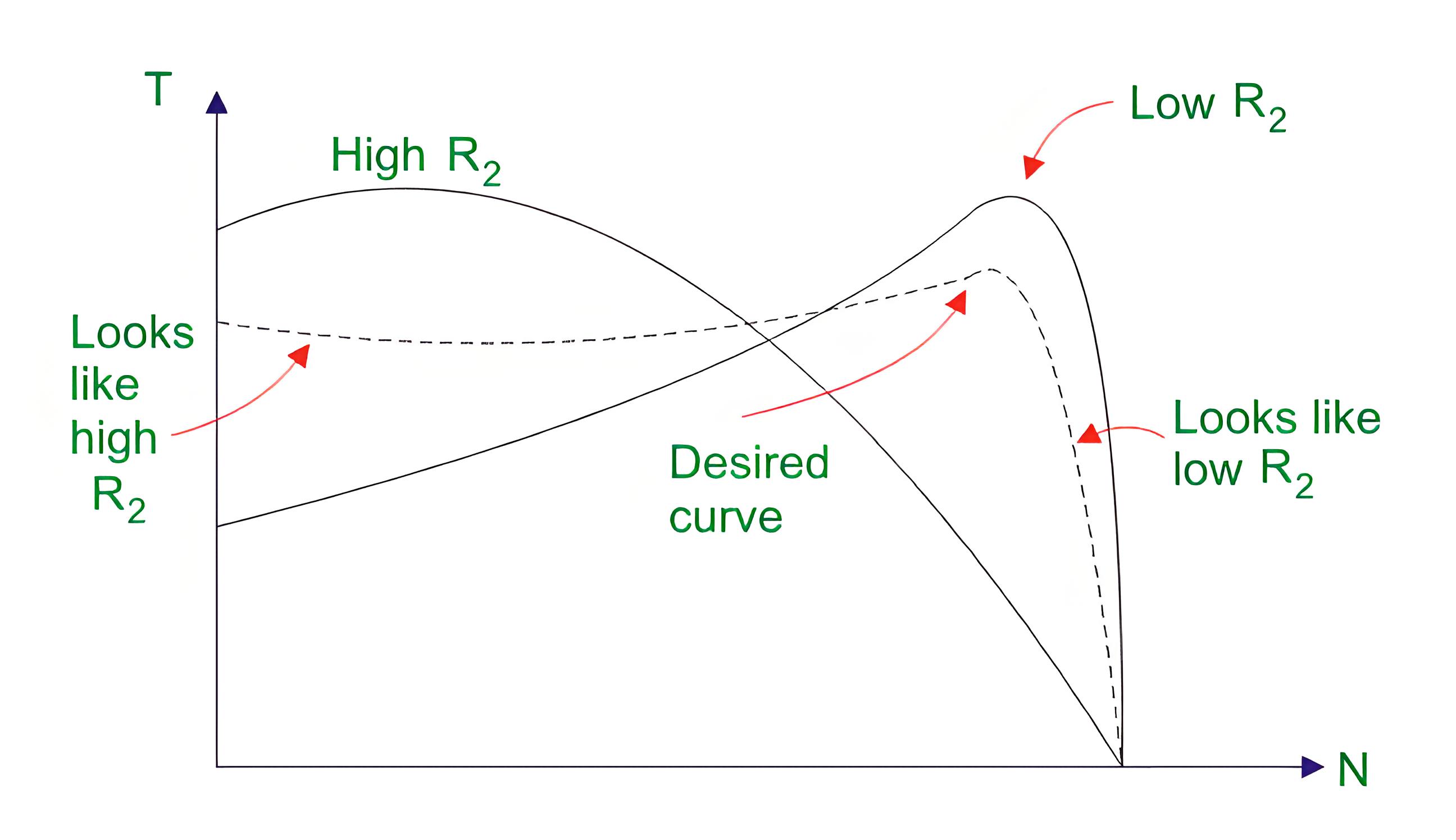
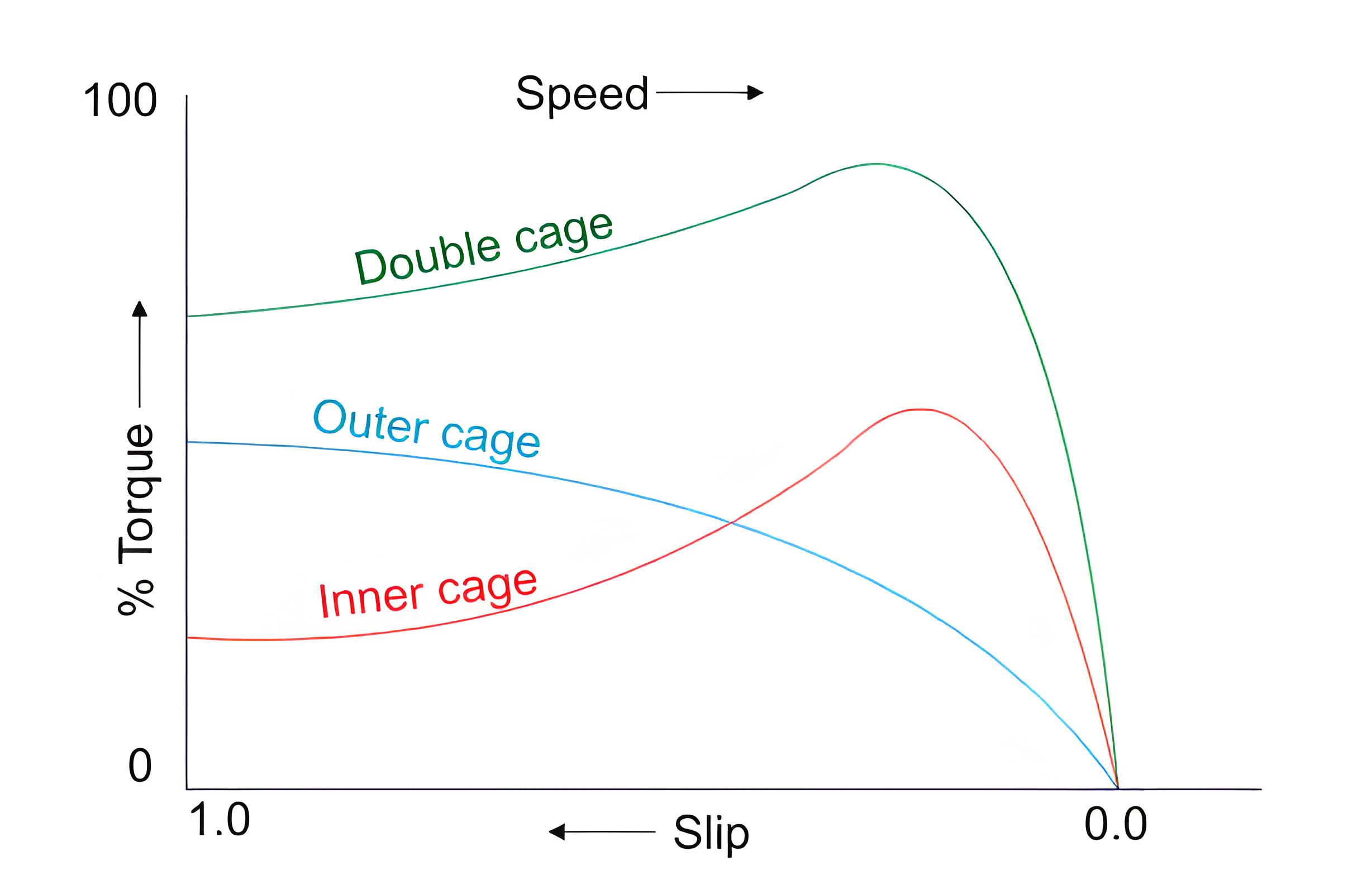
Speed-torque characteristics
Where, R2 and X2 are rotor resistance and inductive reactance at starting, respectively, E2 is rotor induced electromotive force and
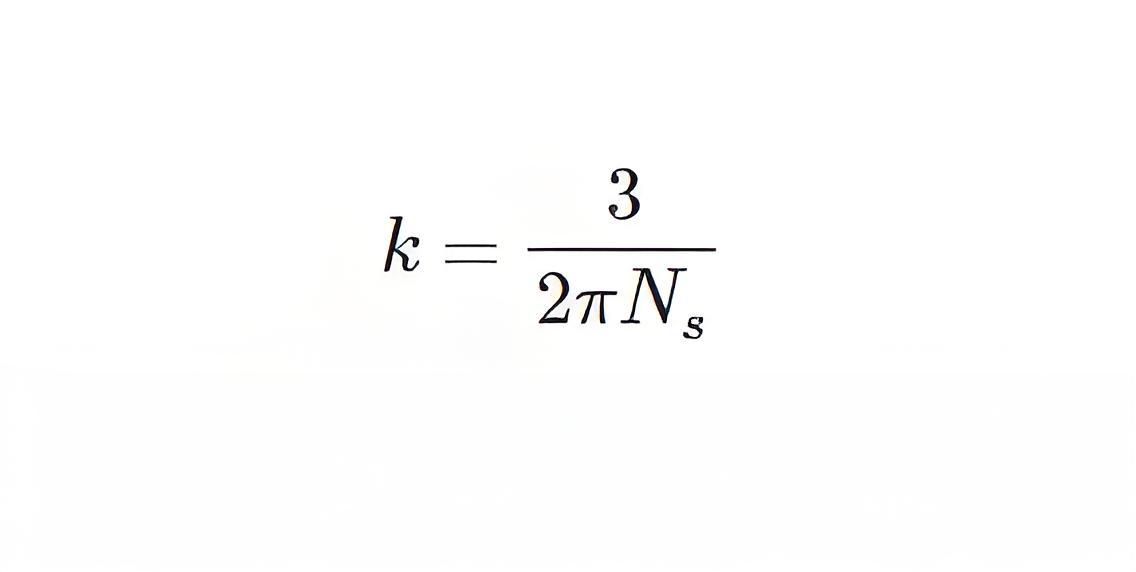
Ns is the RPS speed to synchronize the stator flux, and S is the slip of the rotor speed. The speed-torque diagram above shows that under static conditions, the higher the resistance value, the greater the torque value, and the higher the slip value, the greater the torque.
Comparison of single cage motor and double cage motor
The double cage rotor has low starting current and high starting torque. Therefore, it is more suitable for direct online startup.
Due to the higher effective rotor resistance of the double-cage motor, the rotor heats up more when starting compared to the single-cage motor.
The high resistance of the outer cage increases the resistance of the double cage motor. As a result, full load copper loss increases and efficiency decreases.
The pull out torque of the double cage motor is smaller than that of the single cage motor.
The cost of a double-cage motor is about 20-30% higher than a single-cage motor of the same grade.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.