What is the Differential Protection of Transformers?
What is the Differential Protection of Transformers?
Differential Protection Definition
The differential protection of transformer is an important relay protection method, which is used to detect the faults inside the transformer, such as winding short circuit, turn short circuit and so on. Differential protection determines whether there is a fault by comparing the difference in current on both sides of the transformer.
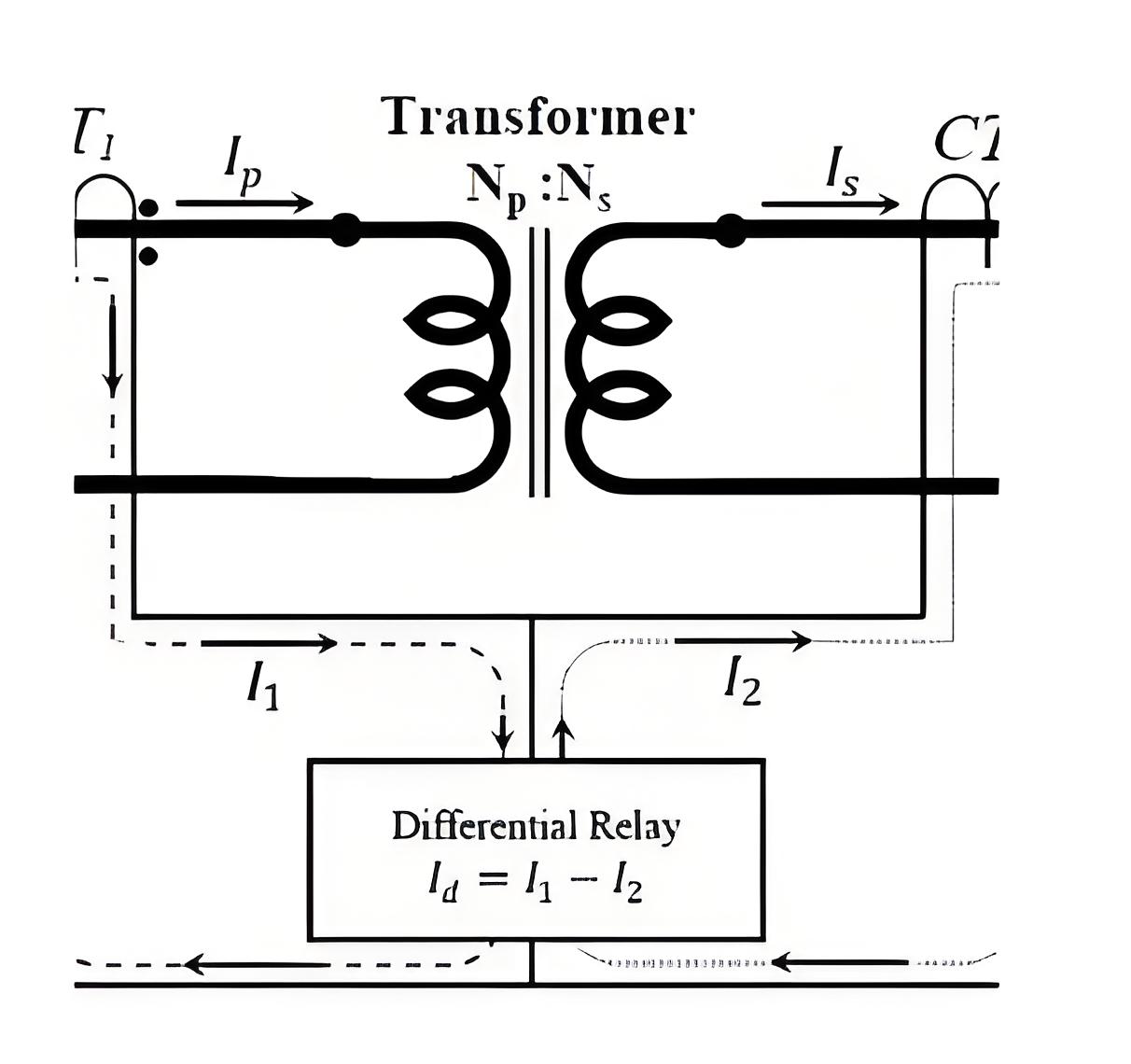
Principle of differential protection
Differential protection is based on a basic principle: under normal operating conditions, the incoming and outgoing currents on both sides of the transformer should be balanced. If a fault occurs inside the transformer, such as a short circuit in the winding, an unbalanced current will be generated in the differential circuit. The differential protective relay detects this unbalanced current to trigger the protective action.
Disposition
Current transformers (CTs) : Current transformers are installed on each side of the transformer to measure current.
Differential relay: The differential relay receives the current signal from the CTs and compares it.
Ratio braking characteristics: Differential relays usually have ratio braking characteristics, that is, the protective action value increases as the unbalanced current increases in the event of an external fault to prevent misoperation.
Operation process
Install current transformer
Install the current transformer on the primary side and the secondary side of the transformer.The polarity of the CTs needs to be properly connected to ensure the correct current flow.
Configuration differential relay
Set the operating threshold of the differential relay.Adjust the parameters of the ratio braking characteristics to suit the specific situation of the transformer.
Monitoring unbalance current
A differential relay continuously monitors the difference in current flowing into and out of the transformer.When the unbalance current exceeds the set threshold, the differential protection will operate.Trigger protection action.When an internal fault is detected, the differential protection triggers a trip, disconnecting the faulty transformer from the grid.
Matters needing attention
Polarity connection: Ensure that the polarity of the current transformer is correctly connected, otherwise it will cause protection misoperation.
Ratio braking characteristics: The ratio braking characteristics are set correctly to prevent misoperation in case of external failure.
Current transformer saturation: In extreme cases such as short circuits, the CTs may become saturated, resulting in protective misoperation.
Winding wiring: Ensure that the winding wiring is correct to avoid unbalanced current.
Maintenance and verification: Maintain and verify differential protection regularly to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
Advantages of differential protection
Fast response: Can quickly detect the transformer internal fault.
Highly selective: It only operates when a fault occurs inside the transformer and is selective to external faults.
High sensitivity: reliable operation even in case of minor internal faults.
Limitations of differential protection
External failure: In the event of an external failure, the differential protection may be affected by an unbalanced current, resulting in misoperation.
CTs saturation: Under extreme high current conditions, CTs may become saturated, affecting the accuracy of protection.
Maintenance and verification
Periodic verification: Periodically verify the differential protection system to ensure that its performance meets the requirements.
Simulation test: Perform simulated fault tests to verify the response capability of the protection system.
CTs maintenance: Periodically check the operating status of the CTs to ensure its accuracy and reliability.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.