How does the dielectric oil tan delta meter work?
Working Principle of Dielectric Loss Tester for Insulating Oil
A dielectric loss tester for insulating oil is an instrument used to measure the dielectric loss factor (tan δ) and capacitance of insulating oil. Its working principle is based on measuring the loss characteristics of insulating oil under an alternating electric field. Here is a detailed explanation of the principle:
Working Principle
Application of Electric Field:
The tester applies an alternating electric field to the insulating oil sample in the test container. Typically, this electric field is generated by a pair of parallel plate capacitors.
Current Measurement:
The current in the capacitor can be divided into two components: displacement current (reactive current) and loss current (active current). Displacement current is related to the capacitance, while loss current is related to the dielectric loss factor.
The displacement current Ic and loss current Id can be distinguished by measuring the total current I and the phase difference ϕ.
Phase Difference Measurement:
By measuring the phase difference ϕ between the applied voltage V and the total current I, the dielectric loss angle δ can be determined.
The dielectric loss factor tanδ is defined as the ratio of the loss current to the displacement current:
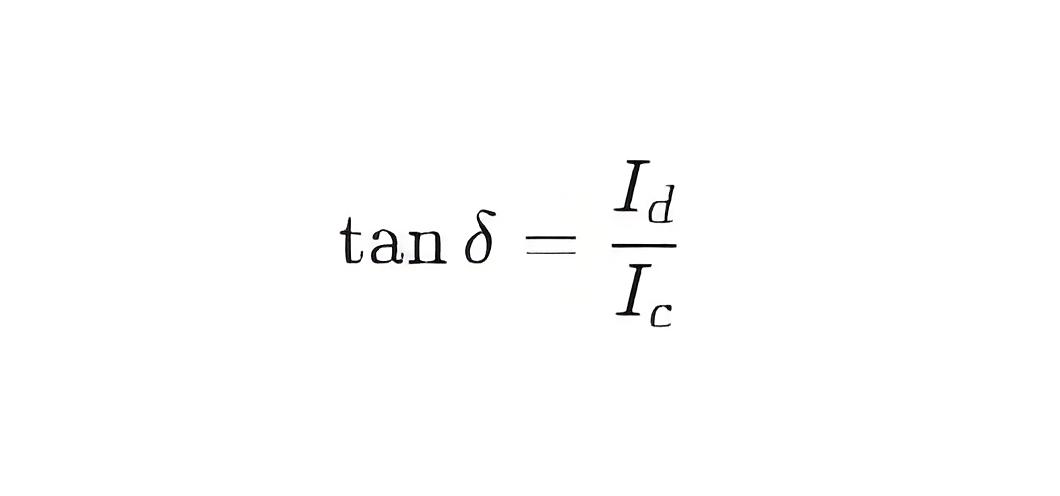
Capacitance Measurement:
The capacitance C of the capacitor can be further verified to assess the quality of the insulating oil. The capacitance can be calculated by measuring the frequency f and the applied voltage I:
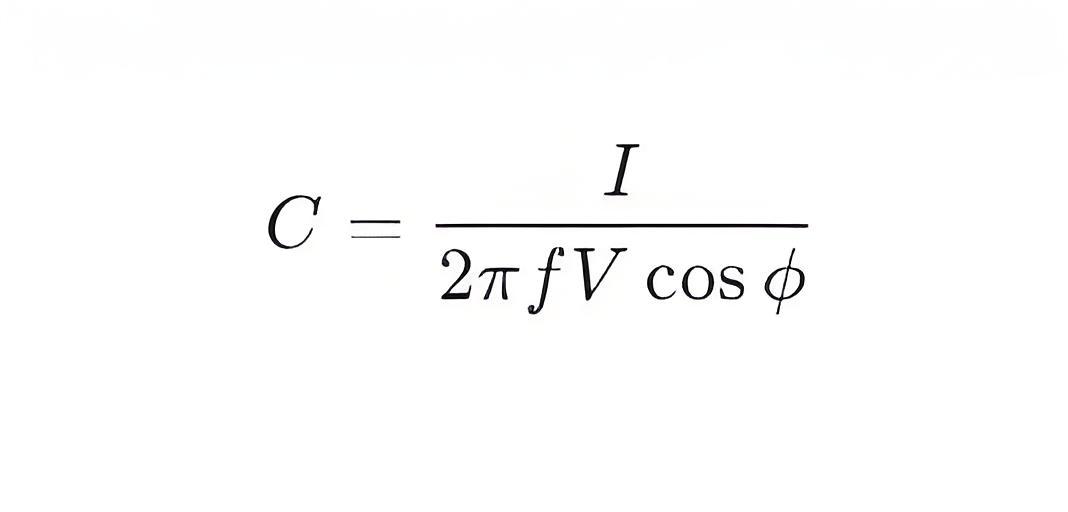
Data Processing:
The built-in data processing unit of the tester calculates the dielectric loss factor tanδ and capacitance C using the above formulas and displays the results.
Significance in Electrical Systems
Insulation Performance Evaluation:
Insulating oil is a critical insulating material in many electrical devices, such as transformers, circuit breakers, and cables. The dielectric loss factor tanδ reflects the aging degree and contamination level of the insulating oil. A high tanδ value indicates that the insulating oil may have deteriorated and needs to be replaced or treated.
Fault Diagnosis:
Regular measurement of the dielectric loss factor can help detect potential faults in electrical equipment, such as partial discharge, moisture ingress, or contamination. This aids in preventing equipment failure, reducing maintenance costs, and minimizing downtime.
Quality Control:
During the production process, a dielectric loss tester can be used to monitor the quality of newly produced insulating oil to ensure it meets standard requirements. This helps improve product reliability and safety.
Maintenance Management:
For electrical equipment already in use, regular measurement of the dielectric loss factor of insulating oil is an important part of maintenance management. This helps in formulating reasonable maintenance plans and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Summary
A dielectric loss tester for insulating oil effectively evaluates the insulation performance of insulating oil by measuring its dielectric loss factor and capacitance. It helps diagnose potential faults in electrical equipment, ensures the safe and reliable operation of electrical systems, and aids in quality control and maintenance management.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.




